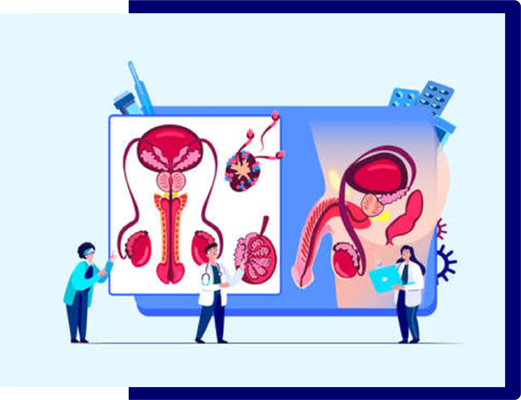
Penile cancer occurs when cells on or in a man's penis grow out of control. It usually begins in skin cells and spreads throughout the body.
It's really uncommon. It can, however, be treated, especially if caught early.
There are around 200 forms of cancers based on the tissue or organ where the cancer develops, and these are referred to as primary cancers. The term "metastasis" refers to the process of cancer spreading from one tissue to another. Malignancies that have migrated from their main sites, or where they first emerged, are known as secondary or metastatic cancers.
Medica’s oncology department excels in providing world-class cancer treatment driven by their collective clinical excellence of over 30+ years. With a multidisciplinary approach to treating all types and forms of cancer, our oncologists and onco-surgeons are supported by the latest cancer treatment technologies along with a team of highly-skilled reconstructive surgeons who deliver extensive treatment to all of our patients, adults and children alike.